1.Switch문
swich 문에 사용된 수식은 정수형 자료(문자포함)이어야 한다.
-case문에 사용되는 값은 오로지 한개의 값만 사용할 수 있다. (2,3이런식으로 연달아 사용 못함.)
-if 문 처럼 논리값을 사용할 수 없다.
-case 문에 실행문이 여러개 나오더라도 {} 중괄호를 사용하지 않는다.
-break문이 없으면 다음 case로 넘어간다.
-default : case에 해당하지 않는 내용을 처리한다.
-비교 대상과 case의 자료형이 동일해야한다.
class Switch_1
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
int a;
System.out.print("1-9사이의 값 입력하시오 : ");
a=System.in.read()-'0'; // 아스키코드번호로 출력됨의로 '0'을 빼서 10진수의 수형태로 바꿈
switch(a)
{case 1 :
System.out.println(a+"홀수입니다.");
break;
case 3:
case 5:
case 7:
case 9:
System.out.println(a+"홀수입니다.");
break;
//이런식으로 여러가지 case를 한꺼번에 다룰수도 있다.
case 2:
case 4:
case 6:
case 8:
System.out.println(a+"짝수입니다.");
break;
default : System.out.println(a+"는 숫자입니다.");
break;
}
}
}class Switch_2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int score = 1;
switch(score*100)
{
case 100 :
System.out.println("당신의 점수는 100 상품은 자전거입니다.");
case 200 :
System.out.println("당신의 점수는 200 상품은 tv입니다.");
case 300 :
System.out.println("당신의 점수는 300 상품은 노트북입니다.");
case 400 :
System.out.println("당신의 점수는 400 상품은 자동차입니다.");
default :
System.out.println("죄송하지만 당신의 상품은 없습니다.");
break;
}
}
}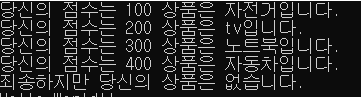
←출력결과
break가 나와야 정지됨. 이처럼 case 100-400은 break문이 없기 때문에 아랫 문장이 실행되고 default문의 break를 만나 정지됨.
Math.random()을 이용한 예제↓↓
class Switch_3
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
char ch = (char)(Math.random()*4+'A');
// char형으로 바꾸면서 정수형이 되므로 소숫점 이하는 절삭됨
//0<=Math.random()*4<4
int score = 0;
switch(ch)
{
case 'A':
score =90;
break;
case 'B':
score = 80;
break;
case 'C' :
score = 70;
break;
case 'D' :
score = 60;
break;
default :
score =0;
break;
}
System.out.println("당신의 점수는 "+score+"입니다.");
}
}
2.Math.random();
- random 클레스와는 달리 별도의 import필요 없음.
- 0.0-1.0사이의 임의의double을 출력하는 것을말함.(난수)/ 중복이 허용된다. 여러번 추출시 중복된 수가 나올수도 있다.
즉 0.0 <=Math.random()<1.0(1은 포함되지 않음에 주의)
- 정수형으로 바꾸면 소숫점이하는 절삭된다.
- 정수 0이상 10이하 표현 방법 : (int)Math.random*11 해주면 된다. (0<= Math.random*11 <11)
- 난수발생 공식
(int)(Math.random()*(최대값 -최소값 +1))+(최소값)
예)
15 이상 50 이하의 수
(int) (Math.random()*(50-15+1))+15
class Switch_4
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int score = (int)(Math.random()*10)+1;
// score가 int형이므로 랜덤값도 형변환 해준다.
String msg = "";
score*=100;
msg ="당신의 점수는 "+score+"이고, 상품은 ";
switch(score)
{
case 700:
msg+="자전거, ";
case 800:
msg+="TV, ";
case 900:
msg+="노트북, ";
case 1000:
msg+="자동차, ";
break;
default :
msg+="볼펜, ";
break;
}
System.out.println(msg+"입니다.");
}
}class random_1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int score = 0;
for(int i =1;i<=100; i++){
score =(int)( Math.random()*101);
//주의할점 : int형으로 변형하려고 int붙일때
//(int)Math.random()*101을 해주면 랜덤을 먼저 정수로 바꾼후 곱하기가 실행됨으로
//랜덤을 인트로 바꾸면 0.숫자 이므로 0이됨
System.out.printf("%5d",score);
if(i%10==0){
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}랜덤 알파벳 100개 출력하기(char)
*주의할점*
ch =(char)( Math.random()*26+'A');
알파벳이 26개니까 26곱하고, 그러면 랜덤이 0이상26미만이 된다.즉 26개의 공간이 생김.
거기에 'A'를 더하는이유는
0+'A'가='A'됨으로 랜덤수가 0,1,2,..가될때 A,B,C...가 출력됨.
class random_Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
char ch = ' ';
for(int i =1;i<=100; i++){
ch =(char)( Math.random()*26+'A');
//알파벳이 26개니까 26곱하고,
//그러면 랜덤이 0이상26미만이 된다. 거기에 'A'를 더하는이유는
//0+'A'가됨으로 랜덤수가 0,1,2,..가될때 A,B,C...가 출력됨.
System.out.printf("%3c",ch);
if(i% 5==0){
//출력할때 5개씩 나오고 줄을 바꿔서 나오게 하기위해
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
-다른방법(형변환 위치가 다름)-
class random_Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int ch = ' ';
for(int i =1;i<=100; i++){
ch =(int)( Math.random()*26+'A');
System.out.printf("%5c",(char)ch);
if(i% 5==0){
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
'KH > JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| #7 while문 (반복문) / do~while (0) | 2022.07.11 |
|---|---|
| #6.for(연습문제) (0) | 2022.07.11 |
| #4 cmd(명령 프롬프트) (0) | 2022.07.07 |
| #3 if else (0) | 2022.07.07 |
| #2 scanner, printf,in.read() (0) | 2022.07.07 |